Pubblicato in News

CEM4 Changelog 2005-2025
CEM4: che cosa abbiamo fatto nelle 185 Versioni dal 2005 a Dicembre 2025.
L'evoluzione di Certifico Macchine 4 / CEM4 dal 2005 al 2025: Tutto quello che è stato fatto dalla Versione 2 alla 4.25.X.
Distribuzione soggetta a Copyright Certifico S.r.l.
- Pubblicato: 22 Gennaio 2026
- Visite: 2726
Pubblicato in News

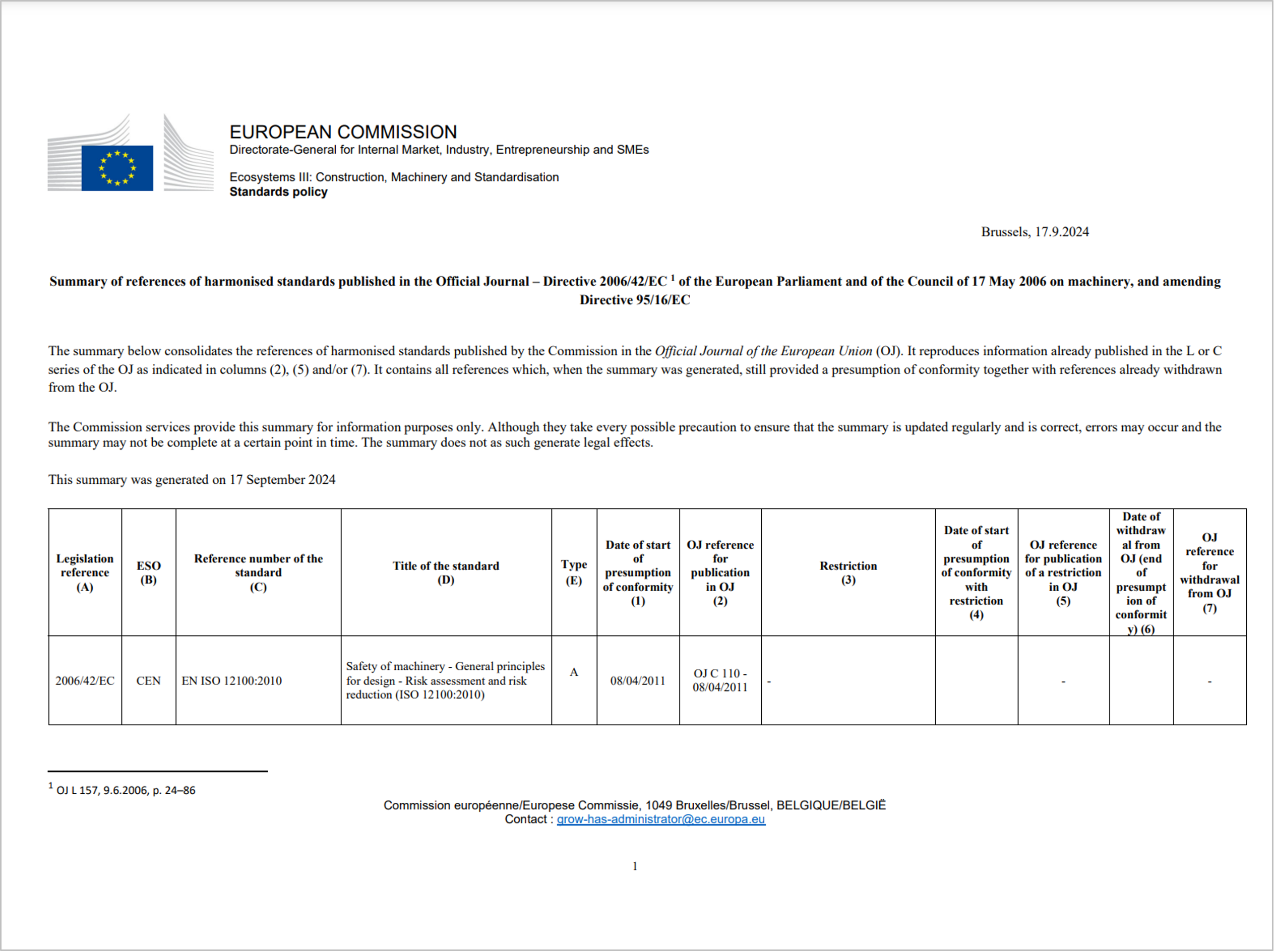
Norme armonizzate Direttiva macchine Gennaio 2026: il File CEM
Update 14.01.2026 | Download scheda
Importa il File CEM in CEM4 e visualizza tutti i titoli delle norme armonizzate per la Direttiva macchine aggiornati a Gennaio 2026
Elenco consolidato dei titoli delle Norme armonizzate per la Direttiva Macchine 2006/42/CE a Gennaio 2026, in formato CEM, che tiene conto delle:
1. Comunicazione C 092 del 9 marzo 2018 (GU C 92/1 del 09 marzo 2018)
2. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2019/436 della Commissione, del 18 marzo 2019 (GU L 75 del 19 marzo 2019)
3. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2019/1766 della Commissione del 23 ottobre 2019 (GU L 270/94 del 24 ottobre 2019)
4. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2019/1863 della Commissione del 6 novembre 2019 (GU L 286/25 07 novembre 2019)
5. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2020/480 della Commissione del 1° Aprile 2020 (GU L 102/6 del 02.04.2020)
6. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2021/377 della Commissione del 2 marzo 2021 (GU L 72/12 del 3.3.2021)
7. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2021/1813 della Commissione del 14 ottobre 2021 (GU L 366/109 del 15.10.2021)
8. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2022/621 della Commissione del 7 aprile 2022 (GU L 115/75 del 13.4.2022)
9. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2023/69 della Commissione del 9 gennaio 2023 (GU L 7/27 del 10.1.2023)
10. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2023/1586 della Commissione del 26 luglio 2023 (GU L 194/45 del 02.08.2023)
11. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2024/1256 della Commissione, del 26 aprile 2024 (GU L 2024/1256 del 30.4.2024)
12. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2024/1329 della Commissione del 13 maggio 2024 (GU L 2024/1329 del 15.5.2024)
13. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2024/2408 della Commissione del 13 settembre 2024 (GU L 2024/2408 del 16.9.2024)
14. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2025/1740 della Commissione del 13 agosto 2025 (GU L 2025/1740 del 14.8.2025)
15. Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2026/80 della Commissione del 12 gennaio 2026 (GU L 2026/80 del 13.1.2026)
Con il file CEM puoi avere sotto controllo in CEM4, nell'Archivio normativa, tutte le Norme armonizzate (n. 936), suddivise per CEN/CENELEC/Tipo A/B/C, consultare, gestire direttamente da CEM4 e commentare le stesse.
Download Norme formato CEM | CEM4.EU
Download Elenco consolidato norme armonizzate PDF
Vedi la nuova sezione "Norme armonizzate click"
Collegati
- Pubblicato: 14 Gennaio 2026
- Visite: 4963
Pubblicato in News

CEN/TR 18058:2024 Guida | Interpretazione EN 619:2022
CEN/TR 18058:2024 - Continuous handling equipment and systems - Safety requirements for equipment for mechanical handling of unit loads - Interpretations relating to EN 619:2022.
Il rapporto tecnico è una raccolta di interpretazioni relative alla norma EN 619:2022 che tratta i requisiti di sicurezza per le apparecchiature di movimentazione meccanica di carichi unitari:
- trasportatori a nastro;
- trasportatori a catena;
- trasportatori a rulli (motorizzati e folli);
- monorotaie;
- traslatori su rotaia.
Le interpretazioni mirano a migliorare la comprensione dei punti a cui fanno riferimento e, in tal modo, a facilitare la comprensione reciproca tra fabbricanti, installatori, organismi notificati, organismi di ispezione e autorità nazionali. Le interpretazioni non hanno lo stesso valore delle norme europee a cui si riferiscono. Tuttavia, l'applicazione delle interpretazioni garantisce alle parti interessate che la norma europea pertinente non sia stata applicata in modo errato.
Il rapporto tecnico non è applicabile alle macchine o ai componenti di macchine fabbricati prima della data della sua pubblicazione.
Nel presente documento sono presenti le schede interpretative tradotte in Italiano.
La norma EN 619:2022 “Apparecchiature e sistemi di movimentazione continua - Requisiti di sicurezza per le apparecchiature di movimentazione meccanica di carichi unitari” tratta i requisiti per la progettazione, il trasporto, l'installazione, la messa in servizio, il funzionamento, la regolazione, la manutenzione e la pulizia della macchina per ridurre al minimo i pericoli elencati nella stessa.
EN 619:2022 Apparecchiature e sistemi di movimentazione continua - Requisiti di sicurezza per le apparecchiature di movimentazione meccanica di carichi unitari.
Data entrata in vigore: 30 marzo 2022
Recepita in Italia da UNI come
UNI EN 619:2022 ed entrata in vigore il 30 giugno 2022.
Con la Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2023/1586 la EN 619:2022 è stata adottata come norma armonizzata per la direttiva 2006/42/CE.
Il presente documento è una traduzione non ufficiale in lingua italiana del CEN/TR 18058:2024 - Traduzione non ufficiale IT.
[...]
- Pubblicato: 10 Dicembre 2025
- Visite: 11367
Pubblicato in News

CEN/TR 18058:2024 - Interpretations relating to EN 619:2022
CEN/TR 18058:2024 - Continuous handling equipment and systems - Safety requirements for equipment for mechanical handling of unit loads - Interpretations relating to EN 619:2022.
Il rapporto tecnico è una raccolta di interpretazioni relative alla norma EN 619:2022 che tratta i requisiti di sicurezza per le apparecchiature di movimentazione meccanica di carichi unitari:
- trasportatori a nastro;
- trasportatori a catena;
- trasportatori a rulli (motorizzati e folli);
- monorotaie;
- traslatori su rotaia.
Le interpretazioni mirano a migliorare la comprensione dei punti a cui fanno riferimento e, in tal modo, a facilitare la comprensione reciproca tra fabbricanti, installatori, organismi notificati, organismi di ispezione e autorità nazionali. Le interpretazioni non hanno lo stesso valore delle norme europee a cui si riferiscono. Tuttavia, l'applicazione delle interpretazioni garantisce alle parti interessate che la norma europea pertinente non sia stata applicata in modo errato.
Il rapporto tecnico non è applicabile alle macchine o ai componenti di macchine fabbricati prima della data della sua pubblicazione.
[...]
- Pubblicato: 27 Novembre 2025
- Visite: 11182
Pubblicato in News

SISTEMA EN ISO 13849-1 Versione 3.0.4 Build 3
Safety Integrity Software Tool for the Evaluation of Machine Applications
Rilasciata da IFA la Versione stabile di SISTEMA (3.0.4 Build 3) a Settembre 2025 aggiornato ad EN ISO 13849-1:2023
Add more
- Pubblicato: 22 Ottobre 2025
- Visite: 17223